
A CLO, or Collateralized Loan Obligation, is a type of financial instrument used to finance corporate loans.
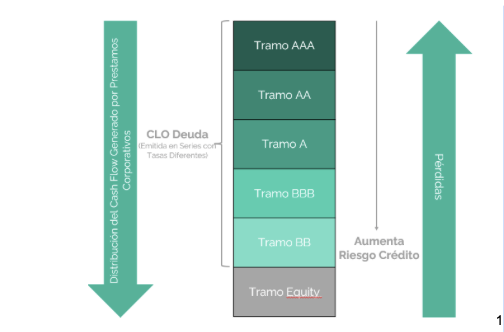
CLOs are issued through a specialized vehicle, which collects loans and divides them into different tranches based on their level of risk. Investors who purchase CLO tranches receive the cash flows of the underlying loans and, in some cases, a share of the appreciation in the value of the loans.
The first time a CLO was issued was during the 1980s, and since then the market has grown significantly, especially in the United States. One of the main characteristics of CLOs is that they are used to buy and finance corporate loans of different risk, at the same time highlighting their scope and diversification that is generally not possible to achieve at the level of an individual investor.
CLOs are also structured in such a way that the cash flows of the underlying loans are divided into different tranches, allowing investors to choose the level of risk and return they desire.
Although CLOs can provide attractive returns, they also have significant risks. One of the biggest risks is default risk, as the underlying loans are often made to companies that have a higher risk of not being able to repay them.
In addition, CLOs are also exposed to macroeconomic risks, such as economic downturns and changes in interest rates. It is important to note that rate changes can also impact the valuation of CLOs.
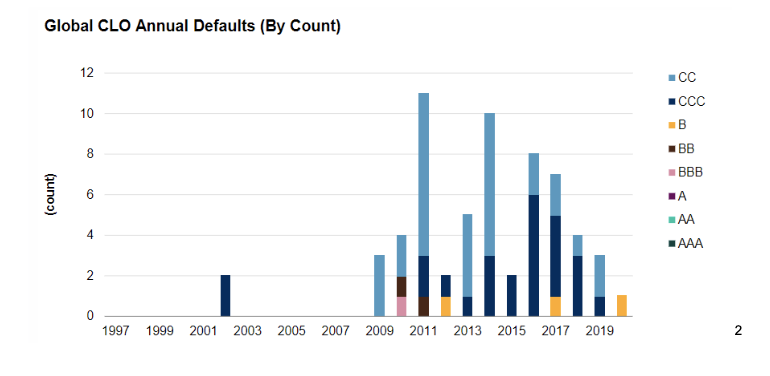
On the other hand, in the period between 2019 and 2020 only 4 CLO defaults were recorded and around 10% recorded a drop in their credit rating. Notwithstanding the above, the historical average of defaults is less than 1%.
Moody's estimates that a possible recession in the US in the second quarter of 2023 and GDP growth of 0.4% would result in a default rate for the lowest-rated issuers of around 5% (versus the previous 12 months, which had a default rate of 1.0%).
These defaults come at the same time as issuer rating downgrades, particularly in the BBB to CCC tranches.
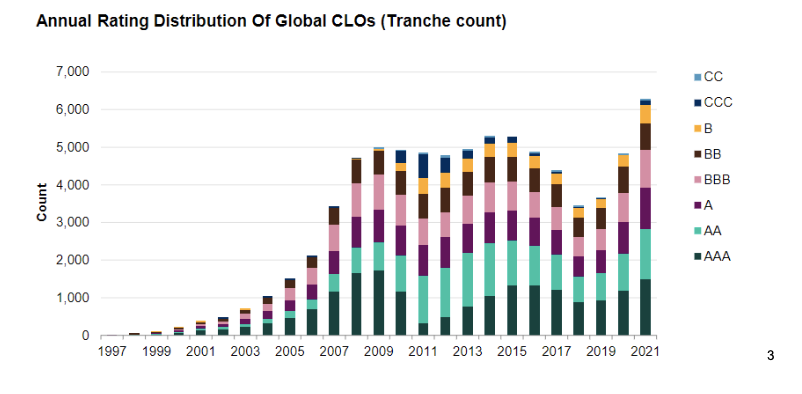
The CLO market is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. In addition, many institutional investors, such as pension funds and hedge funds, have specific requirements to invest in CLOs. Major CLO managers and issuers include Blackstone, Carlyle Group and KKR, among others.
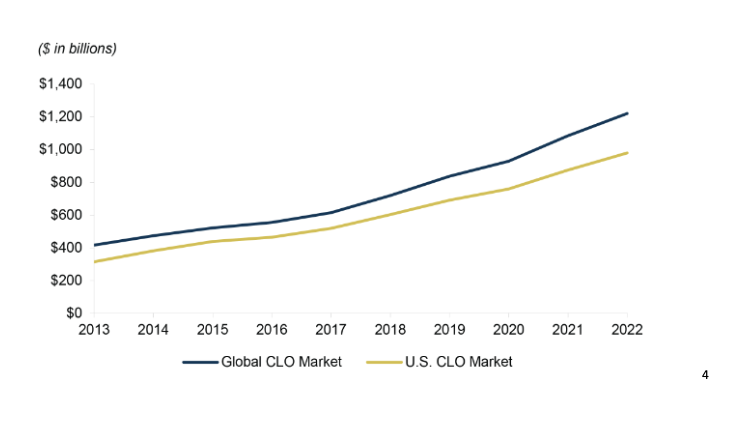
The CLO market in the United States is large and complex. In 2020, more than US$125bn in CLOs were issued in the United States. However, the market has also been subject to criticism and regulatory absence due to its role in the 2008 financial crisis.
Despite these risks and challenges, CLOs continue to be an important source of financing for high-risk companies and an investment option for institutional investors.
Martín León
Deputy Manager of International Funds Fynsa AGF